
| Gust Factor |  |
The gust factor is the ratio of the maximum wind speed that occurs within a time step to the mean wind speed in that time step:
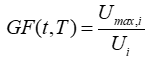
where: | ||
| T | is the length of time step [s] | |
| t | is the gust averaging time [s] | |
| Ui | is the mean wind speed in time step i [m/s] | |
| Umax,i | is the maximum wind gust (averaged over t seconds) that occurs in time step i [m/s] |
The gust averaging time will affect the 'maximum wind speed' or 'maximum gust' measured in a time step. The maximum one-second gust, meaning the maximum speed averaged over a one-second interval, will exceed the maximum three-second gust, which will in turn exceed the maximum 30-second gust.
When calculating high wind hysteresis effects on wind turbine power production, Windographer sometimes needs to estimate the gust factor for different gust averaging times. It offers three options for doing so: the extended Wieringa equation, the Gauss-Weibull equation, and the AWST gust factor equation.
The extended Wieringa equation gives the gust factor in a particular time step as a function of time step length, gust averaging time, and the turbulence intensity in the time step:
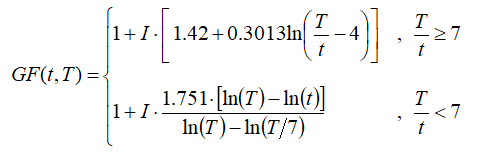
where: | ||
| GF | is the gust factor [unitless] | |
| I | is the turbulence intensity [unitless] | |
| T | is the length of time step [s] | |
| t | is the gust averaging time [s] |
The Gauss-Weibull equation also gives the gust factor in a particular time step as a function of time step length, gust averaging time, and the turbulence intensity in the time step:
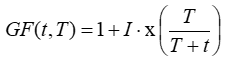
where: | ||
| GF(t,T) | is the gust factor for averaging time t in time step T [unitless] | |
| t | is the gust averaging time [s] | |
| T | is the length of time step [s] | |
| I | is the turbulence intensity [unitless] | |
| x() | is the quantile function of the standard normal distribution |
AWS Truepower developed an equation, specific to 10-minute time steps, to approximate the gust factor for any gust averaging interval t:
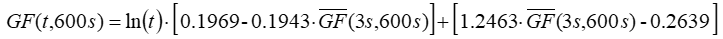
where: | ||
| t | is the gust averaging time [s] | |
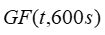 | is the gust factor for 10-minute time steps for gust averaging time t [unitless] | |
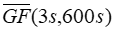 | is the observed mean 3-second gust factor in the time series of 10-minute time steps [unitless] |
To generalize this equation for use with any time step, we can divide GF(t,600s) by GF(T,600s), which is the output of the above equation setting t = T. The generalized form of the AWST gust factor equation is therefore:
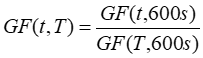
Note: unlike the other two gust factor equations, the AWST gust factor equation produces a constant gust factor, which depends only on the time step, the gust averaging time, and the observed mean 3-second gust factor.
See also