
| Wind Veer Rate |  |
The wind veer rate is a measure of how quickly the wind direction changes with height above ground. Windographer can calculate the wind veer rate only if the dataset contains two or more wind direction sensors at different measurement heights. It reports the wind veer rate in terms of degrees per 100 vertical metres. A positive value indicates that the wind veers in a clockwise direction with increasing height.
To calculate the wind veer rate, Windographer calculates the vector mean wind direction for each wind direction sensor, then fits a straight line through the graph of vector mean wind direction versus height. The slope of that line equals the wind veer rate.
The screenshot below shows a case where the vector mean wind direction increases with height above ground at a rate of 8.85°/100m, so the wind veer rate is positive 8.85°/100m:
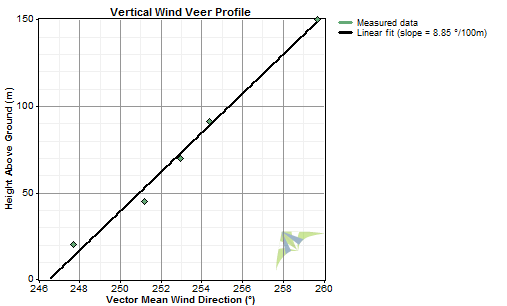
Note that though the above graph shows height on the y-axis, following the convention that Windographer uses whenever plotting height-related data, the least squares calculation of the line of best fit puts the vector mean direction on the y-axis and the height on the x-axis.
The wind veer rate tends to depend on the character of the surrounding terrain and the stability of the atmosphere, as does the wind speed shear. The Wind Shear window shows how the wind veer rate varies with month, time of day, direction, and other factors. It also lets you analyze the frequency of extreme wind veer events.
Tip: In the Configure Dataset window you can create a calculated data column containing the wind veer rate in every time step of the dataset.
See also
Wind veery rate calculated column