
| Inflow Angle |  |
The inflow angle is the angle that the wind speed vector makes with the horizontal. It's the angle at which the wind would flow into a wind turbine. A positive vertical wind speed results in a positive inflow angle, as in the diagram below:
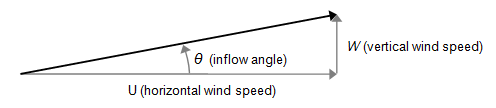
Windographer calculates the inflow angle using the following equation:
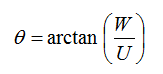
where: | ||
| U | is the horizontal wind speed | |
| W | is the vertical wind speed |
In the Configure Dataset window you can instruct Windographer to calculate the infow angle in every time step of the dataset, and add that time series to the dataset as a calculated data column. The dataset must contain wind speed data and vertical wind speed.
You can choose with horizontal and vertical wind speed data columns to include in the Calculated Data Column Properties window as shown below:
Whenever you change either of these data columns, for example by flagging a segment, deleting a segment, applying a scale factor, or appending more data, Windographer will re-calculate the inflow angle and any other calculated column that depends on the wind speed data. Note that the calculated data column will have no data when either original data column is missing or flagged to exclude from calculations.
See also