
HOMER Pro 3.16

You can import a load from a time-series file using one of several formats that HOMER Pro recognizes.
Tip: You can import data with any time step down to one minute. HOMER detects the time step based on the number of rows in the file. For example, if the data file contains 8760 lines, HOMER assumes it is hourly data. If the data file contains 35,540 lines, HOMER assumes it is 15-minute interval data.
On the Electrical, Thermal, or Hydrogen Set Up page:
•Click the Import button to quickly import a simple time series file.
•Click the Import and Edit button to import data files with gaps in the data or an incorrect number of rows. This function includes basic gap-filling tools to fill in missing data points.
Import
HOMER Pro can recognize several layouts of a .csv file, as listed in the accepted format section below.
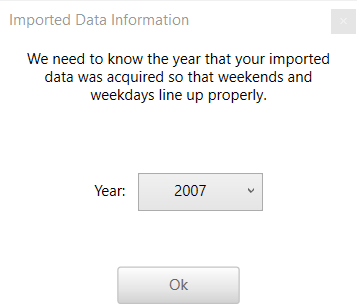
The import function requires having data that consists of 365 consecutive days. The data will be automatically imported if possible. Set this to the year that you want to simulate. Data that can have different weekday/weekend behavior, such as loads, schedules, and tariffs, are shifted to match the modeled year. When multi-year is enabled, this is the first year and successive years are incremented and shifted to appropriately
Data must correspond to a valid time step. Valid time steps divide evenly into sixty, so the data must be a corresponding multiple of 8760. If there is more than 365 days of data (up to 10%), the extra values are ignored and the first 365 days are imported. If there is more than 10% of extra data, the time step becomes ambiguous and you will be prompted to use Import and Edit. Likewise, if there are fewer than 8760 values, there is not a full year of data and you will also be prompted to use Import and Edit.
If there is date information and the starting time step is not January 1 0:00, so it goes from the middle of one year to the middle of the next year, the data will be shifted so that it represents a single calendar year. It will be shifted so that it starts on January 1 of the year with more data in such a way that the days of the week still line up correctly.
When you import data from a text file, HOMER makes a copy of the data set and integrates it with the HOMER (.homer) file. After the data is part of the HOMER file, HOMER no longer refers to the original file. If you modify data in the original file, you must import the modified file so the modifications are included in the HOMER file. After you import a data file, HOMER calculates the average 24-hour load profile for the whole year, and displays it in the table and graph. HOMER also displays the name of the imported data file in the title of the load profile graph.
If you click "Enter daily load profile(s)" after importing data from a file, HOMER discards the data from the imported file and synthesizes new data based on the twelve monthly average load profiles it calculated from the imported data. You can edit synthesized data by selecting the month and changing values in the load profile table. To edit values from an imported file, you must edit the file directly and then import the modified file, as described above.
HOMER Pro can recognize several layouts of a .csv file: 1) Two Column Format, 2) Three Column Format, 3) Green Button Format, 4) Utility API Format, 5) Day By Row, 6) Single Column of Values (.txt or .csv file).
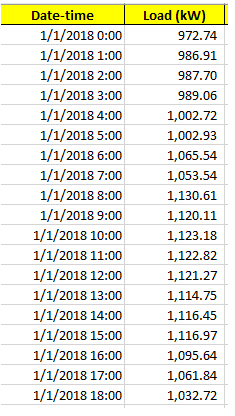
Option 1: Two Column Format
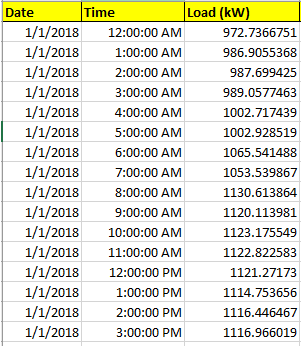
Option 2: Three-column Format
Option 3: Green Button Format
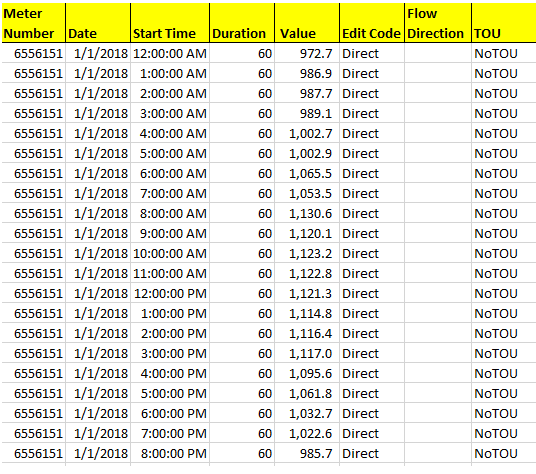
Option 4: Utility API Format
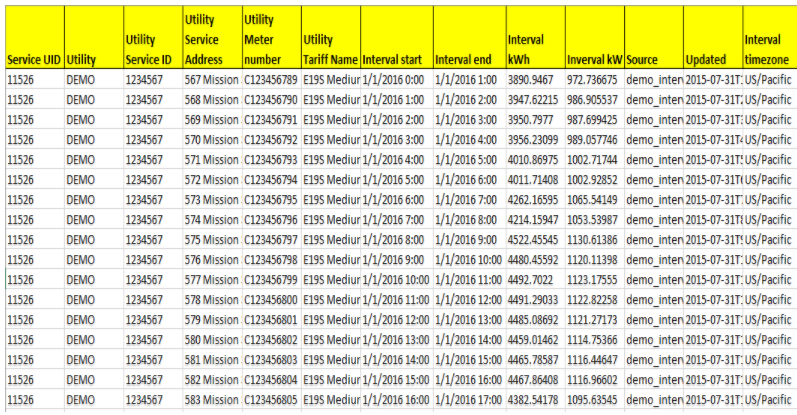
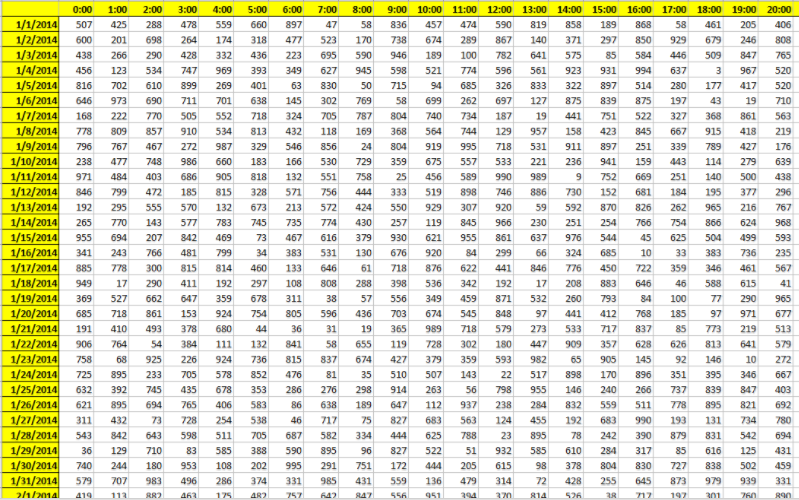
Option 5: Day By Row
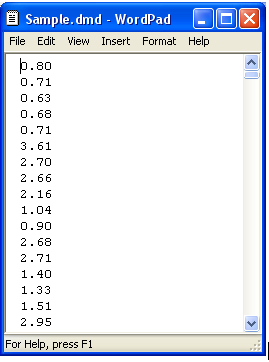
Option 6: Single Column of Values
The .txt or .csv data file must contain a single value on each line, where each line corresponds to one time step. Each value in the file represents the average load (in kW) for that time step. The first time step starts at midnight on Monday, January 1st. The following is an example input file.
Import
HOMER Pro can recognize several layouts of a .csv file, as listed in the accepted formats section below.
The import function requires having data that consists of 365 consecutive days. The data will be automatically imported if possible. If the time step cannot be determined, you will be prompted to use Import and Edit. If the date cannot be determined, you will be asked to provide the year and it will be assumed that the data begins on January 1 0:00.
Data must correspond to a valid time step. Valid time steps divide evenly into sixty, so the data must be a corresponding multiple of 8760. If there is more than 365 days of data (up to 10%), the extra values are ignored and the first 365 days are imported. If there is more than 10% of extra data, the time step becomes ambiguous and you will be prompted to use Import and Edit. Likewise, if there are fewer than 8760 values, there is not a full year of data and you will also be prompted to use Import and Edit.
If there is date information and the starting time step is not January 1 0:00, so it goes from the middle of one year to the middle of the next year, the data will be shifted so that it represents a single calendar year. It will be shifted so that it starts on January 1 of the year with more data in such a way that the days of the week still line up correctly.
The following are examples of weekday/weekend sensitivity:
•Imported grid outage time series with weekend or weekday bias
•Imported grid real-time rates with weekend/weekday differences
•Thermal, hydrogen, or other electric loads with weekend/weekday differences
•Imported biomass resource time series with weekend/weekday bias
•Generators and electrolyzers with an operation schedule (forced on, forced off, or optimized) with weekend/weekday differences
Note: Natural resources generally do not have weekend/weekday bias (for example, wind speed is no higher or lower, on average, on weekends than weekdays).
If none of the conditions above apply to your model, use the default year.
Import and Edit
Import and Edit recognizes the same formats as Import and imports the data in the same fashion. Like Import, if it cannot determine the year, it asks you to provide it, it removes extra days, and it shifts the data to represent a calendar year.
Import and Edit also imports data that cannot be handled by Import. If it cannot determine the time step, it will make its best guess and read all of the data. It also accepts gaps in data, detected as blank lines in the file, which can stem from meter failures.
Once the data is read, it is displayed in the Import and Edit view. If the time step is incorrect, you can change it with the Time step (minutes) drop down menu.
Select Grid to modify individual values. You can use a limited set of actions, such as selecting multiple cells and deleting them or copying them to another location. Modified cells are colored green, gaps are red, and deleted cells are yellow.
You can fill gaps and deleted cells with zeros or by linear interpolation.
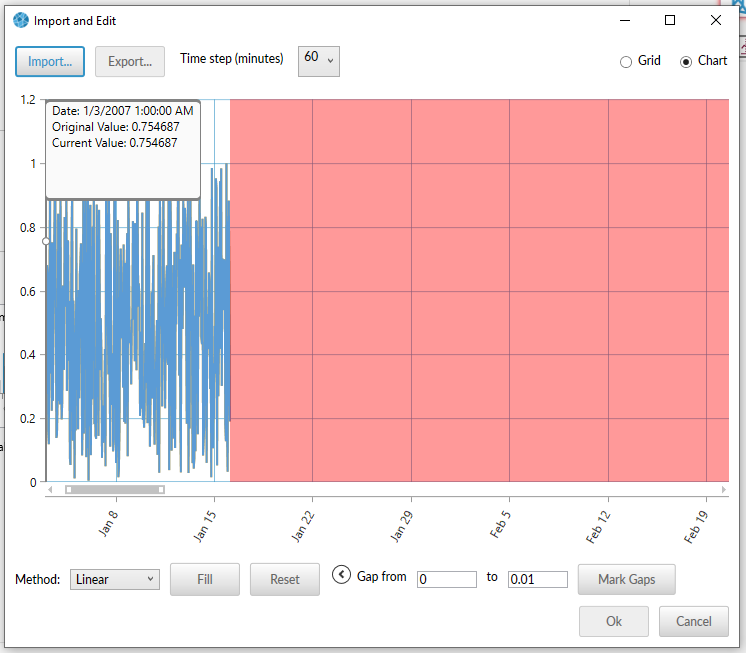
You can mark gaps if you select the (>) as shown below.

Time step (minutes): Ensure that HOMER has correctly identified the duration of timesteps in the uploaded data.
(Advanced expander) If there are any values in the uploaded time series which should be marked as gaps, specify the range of values which should be marked as gaps. For example, if the time series data collector specifies that the collector was offline by assigning a value of negative one to that time-step, you could choose to replace all values of -1 with a gap, and then you can fill that gap linearly or with zeros.
Filling gaps in the data: Choose the method in which the data gaps should be filled, either linearly from the last available value or with zeros. Click "Fill" to assign values to the gaps; click "Reset" to revert the file to as it was originally imported.
Import button: If you want to upload a different file, click "Import..."
Export button: Once you've cleaned the time-series data by identifying faulty time-series values and by filling gaps in the data, you may want to export the time-series information into a .txt file.
