
HOMER Pro 3.16

![]()
The Hydrokinetic Resource page allows you to describe the flow available to the hydrokinetic turbine. HOMER uses this data to calculate the output of the hydro turbine in each time step.
Click the Hydrokinetic button under the Resources tab in the toolbar at the top of the page. The Hydrokinetic Resource page appears.
Choose Water Speed Data Source
The baseline data is a one-year time series representing the water speed, expressed in meters per second, for each time step of the year. HOMER displays the monthly averages calculated from the baseline data in the Monthly Average Water Speed Data table and graph.
There are two ways to create baseline data: you can enter monthly averages, or you can import time series data from a file.
Click either the Enter monthly averages radio button or the Import from a time series data file or the library radio button.
Enter Monthly Averages
To enter twelve monthly averages, enter each month's average water speed (m/s) in the appropriate row on the Monthly Average Water Speed Data table. As you enter values in the table, HOMER builds a set of 8,760 values, or one water speed value for each hour of the year. HOMER creates the hourly values by assuming that the stream flow is constant throughout each month; HOMER assigns the monthly average value to each hour in that month.
Import Water Speed Data
To import a file, you must prepare a text file that contains the water speed in each time step for a complete year.
Tip: You can import data with any time step down to one minute. HOMER detects the time step when you import the data file. For example, if the data file contains 8760 lines, HOMER assumes it contains hourly data. If the data file contains 52,560 lines, HOMER assumes it contains 10-minute data.
The data file must contain a single value on each line, corresponding to one time step. Each value in the file represents the average water speed (in m/s) for that time step. The first time step starts at midnight on January 1st. The following is a sample input file.
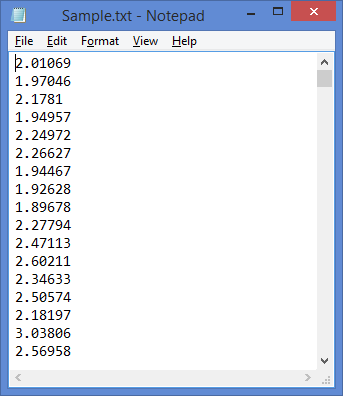
Click the Import button or the Import and Edit button to open the text file. You can import a text file with any extension.
When you import data from a text file, HOMER makes a copy of the data set and integrates it with the HOMER (.homer) file. After the data is part of the HOMER file, HOMER no longer refers to the original text file. If you modify data in the original file, you must import the modified file in order for the modification to be included in the HOMER file. After you import a data file, HOMER calculates twelve monthly average water speed values and displays them in the table and graph. You can view a plot of the time series data by clicking the Plot... button at the bottom of the page.
Scaled Data for Simulation
HOMER uses scaled data for calculations. To create scaled data, HOMER multiplies each of the baseline data values by a common factor that results in an annual average value equal to the value that you specify in the Scaled Annual Average box.

To determine the value of this factor, HOMER divides the Scaled Annual Average by the baseline annual average. The scaled data retains the shape and statistical characteristics of the baseline data, but may differ in magnitude. The default value for the Scaled Annual Average is the baseline annual average. When the two values are equal, the scaled data and baseline are identical. HOMER interprets a Scaled Annual Average of zero to mean that there is no stream flow.
You can use the Scaled Annual Average for unit conversion. For example, you could convert data from an imported file that contains water speed data expressed in miles per hour. If the baseline annual average is 4 mi/hr, enter 1.79 in the Scaled Annual Average box, so the scaled data is equivalent to the baseline data, but expressed in m/s rather than miles per hour: 1 m/s = 2.24 mi/hr; 1.79 m/s = 4 mi/hr.
Another reason to scale the baseline data is to perform a sensitivity analysis on the hydro resource. Click the sensitivities button (to the right of the text box) to enter multiple values for a sensitivity analysis.
The Plot button allows you to view the scaled data in several graphical formats.
See also
